You’re ready to start planting vegetables, but you can’t just go ahead and plant a variety of healthy veggies in your garden whenever you get the urge to do so.
You need to ensure that you’re planting them at the right times to encourage them to grow and be healthy.
When should you start a veggie garden?
Usually, the best time to start a veggie garden is around April or May, but there are some important things to bear in mind depending on where you live and what veggies you want to grow.
So, with that in mind, let’s take a look at everything you need to know about vegetable planting seasons and how to plan ahead to ensure you have a thriving garden.
Table of Contents
The Two Types Of Vegetable Crops To Know About
There are two types of crops: warm-season crops and cool-season crops. The time at which you plant these in your garden will vary because these crops can handle different temperatures.
Warm-Season Crops

Warm crops will grow well during the warmer seasons – late spring, summer, and early fall – when the temperatures are moderate.
You must plant warm-season crops after the last frost, or when those really cold temperatures of winter are over. This will enable your plants to reach maturity so that they’ll be able to be harvested before the first frost of the next cold season.
There are two types of warm-season crops: tender and very tender vegetables.
- Tender veggies, such as sweetcorn, should be planted about a week or two after the last frost has occurred.
- Very tender veggies, such as eggplant and sweet potatoes, should be planted three weeks after the last frost.
Pro tip: You can stimulate warm-season crops to grow slowly into the season of fall by covering them with row covers or cold frames to protect them against harsh conditions such as frost.
What Temperatures Are Best For Warm-Season Crops?
Warm-season veggies need a soil planting temperature that’s a minimum of 50 degrees Fahrenheit, but the temperature is ideal when it’s 60 degrees Fahrenheit. Warm-season crops will thrive when both the air and soil temperature is between 65 and 86 degrees Fahrenheit.
Cool-Season Crops

Cool-season crops fare better when the weather is colder. They will grow best in early spring, late summer, and autumn. These crops need to reach maturity when the weather is still cool otherwise they will end up going to seed, so make sure you plant them when the warm season is tapering off and the colder weather is starting.
There are two types of cool-season crops: hardy and half-hardy crops.
- Hardy crops, such as onions, garlic, and broccoli should be planted between two and four weeks before the last frost during the spring.
- Half-hardy crops, such as carrots, beetroots, and potatoes, are less tolerant to very cold weather so you want to plant them around the time of the last frost in spring.
Pro tip: If you live in a warm region and you want to plant cool-season veggies, make sure you do so late in winter or early in the spring. Then, plant seeds again later in the fall season so that you’ll be able to harvest them in winter.
What Temperatures Are Best For Cool Crops?
Cool-season veggies need a minimum planting temperature that’s between 40 and 50 degrees Fahrenheit. They also grow at their best potential when the temperature has highs of 70 to 75 degrees Fahrenheit.
What To Know about Hardiness Zones And Planting Veggies
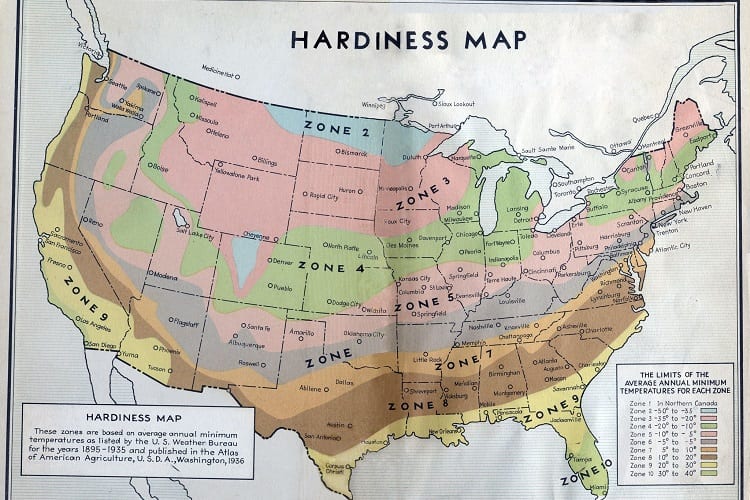
The U.S. Department of Agriculture has set up a system known as “Plant Hardiness Zones” that divides different areas in North America into zones that are based on the coldest temperatures that they experience.
The zones go from Zone 1 (which is the coldest) to Zone 11 (which is the warmest). What you plant will depend on what zone you live in. Let’s look at what the temperatures are like in each of the zones.
- Zone 1: Plants in this zone can handle temperatures that are below -60 degrees Fahrenheit to -50 degrees Fahrenheit. That’s really cold!
- Zone 2: Plants in Zone 2 can handle temperatures of between -40 to -50 Fahrenheit.
- Zone 3: Zone 3 plants can tolerate temperatures of -40 to -30 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 4: These plants can handle temperatures of -30 to -20 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 5: These plants can tolerate temps of between -20 to -10 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 6: These plants can handle temperatures of between -10 to 0 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 7: Now we’re getting warmer! Zone 7 plants can deal with temperatures of between 0 and 10 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 8: Plants in this zone can handle temperatures of between 10 and 20 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Zone 9: Here, plants can deal well in 20 to 30 degree Fahrenheit temperatures.
- Zone 10: Plants in this zone can handle temperatures of between 30 and 40 degrees.
- Zone 11: 40 to 50 degrees Fahrenheit is perfect for plants in this region.
When you purchase a plant seed packet or a plant, there will usually be information about what zone is right for it on the packet or its tag.
Knowing what your zone is can help you to choose the right plants or make sure that you enable the correct growing conditions for whatever you want to grow.
What Veggies To Plant Depending On The Season

Veggies To Plant In Early Spring
If you want to get a head-start on your harvest, there are some vegetables you can grow early on in the spring so that they will thrive, even though it’s usually still too cold at this time of the year for many other vegetable plants to grow.
Plants that you can put in the ground in early spring include asparagus, lettuce, peas, rhubarb, and spinach.
Vegetables To Plant In Summer
Some vegetables thrive on the hot weather, so make sure you plant these veggies in your garden when the weather warms up nicely: sweet potatoes, Southern peas, hot peppers, and okra.
Vegetables To Plant In The Fall
When the weather starts to cool down, you should plant some veggies that will enjoy the cooler temperatures. These include kale, Swiss Chard, leeks, and cauliflower.
How To Look After Your Vegetable Garden
Once you’ve planted veggies in your garden, it’s essential to look after them in the right way so that they can thrive and give you a wonderful harvest.
When To Water Your Vegetable Garden

Follow these tips to ensure that your vegetables are getting enough water.
- Give them an inch of water every week. This is a good rule to follow, but twice a week you should give your vegetables a deeper watering – try to give them about six inches of water so you can ensure the water reaches deeper into their soil.
- Make use of a rain gauge. If there’s been good rainfall in your area recently, you should use a rain gauge as this will help you to see how much rain your garden has really been getting and will help you to adjust how much you need to water your veggie garden.
- Water your garden in the early morning. Forget about watering your garden in the evenings, as this has many disadvantages, such as causing fungus in your plants. Rather water your garden in the early mornings. Your plants will have time to dry out during the day, which will prevent fungus from setting in.
When To Fertilize Your Vegetable Garden

Another important task you need to do is fertilize your vegetable garden so that your plants will receive the nutrients they need to flourish.
Here’s how to fertilize your garden according to the season you’re in so you can give your plants exactly what they want when they want it!
Fertilization Tips During Winter
You want to prepare your garden for summer during winter, such as by removing crops and adding a slow-release fertilizer to the soil that has 10 percent of the following nutrients: potassium, phosphorus, and nitrogen.
After working the fertilizer into the soil, you want to cover it with mulch. This ensures that during the cold months the fertilizer will be released into the soil, prepping it for when spring arrives.
Fertilization Tips During Spring
If you have cool-weather crops that you want to grow and they have a short growing season, such as broccoli and lettuce, they don’t need to be fertilized if the ground was fertilized in winter.
If you forgot to fertilize your veggie beds during winter, now’s the time to give them a quick-release fertilizer that has 10 percent potassium, nitrogen, and phosphorus in it.
Fertilization Tips For Summer
For summer veggies, you might need to give your veggies a bit more nutrition to meet their needs. This is because, as SFGate points out, most summer veggies are heavy feeders.
To ensure they get all the nutrients they need, you want to put slow-release fertilizer in the soil when you plant your summer garden and then give your plants quick-release fertilizer every few weeks.
If you live in an area that’s been affected by drought or severe heat, you’ll need to give your plants some help to draw the nutrients they need from the soil, which can be difficult for them during such conditions.
Here’s a tip to help them along: add a tablespoon of Epsom salt to one gallon of water and apply this to the base of all your plants.
Fertilizer Tips For Fall
When your summer crops are removed, you can start prepping your new veggie garden during the fall. Apply slow-release fertilizer into the soil before you plant new veggies.
Short-season veggies will need less fertilizer, but you can add a quick-release fertilizer every few weeks in the season to increase their production.
Avoid fertilizing your soil after the first frost of the season – this is because the cold temperature will add stress to your veggie plants and if you’re also trying to enhance their growth at the same time, this can be too much for them to handle, causing them to die off.
What To Know About Quick-Growing Vegetables

Some vegetables can be really quick and easy to grow.
If you want to grow and harvest veggies in a short period of time, such as if you hope to maintain the productivity of your veggie garden to make use of the warm weather, then you should grow crops that will take a few weeks to reach harvest.
These include:
- Snap beans, which can grow in 50 days.
- Beetroot, which can also reach harvest in about 50 or so days.
- Summer squash. Some early summer squash varieties will harvest in 40 days, so look for varieties such as ‘Raven’ and ‘Yellow Crookneck.’
- Radishes. These veggies are known for being a vegetable that grows really quickly – you can harvest radishes within 28 days!
How To Grow Vegetables Indoors

Should you grow veggies indoors or in a greenhouse?
Yes! Doing this gives you more control of the growing process. By ensuring your indoor plants have enough light they need to grow, you can grow leafy greens and herbs without a problem.
The average windowsill will offer enough light for plants that need medium amounts of it.
However, if you want to germinate seeds or grow veggies that need a lot of light, such as tomatoes or basil, you’ll need to invest in grow lamps to give these plants more light to meet their needs, as Gardeners reports.
While you might have to tweak how much light your plants receive in order to ensure they get enough, and monitor your watering of them, a benefit of growing vegetables indoors includes fewer pests!
In addition to that, indoor plants are not affected by potentially damaging weather, such as strong winds and frost.
Starting your seeds in the house or a greenhouse helps to give your plants a head-start that could encourage them to have an earlier harvest. This is because they can grow in a controlled environment and by the time they’re transplanted into the garden outside, they’ll be in a stronger position to flourish.
Here are some general guidelines to consider when starting an indoor or greenhouse garden:
Go green(house)!
Making use of a greenhouse is beneficial because it can help you to start the growing season for your veggies earlier in the year, around January or February.
When the first frost comes, you can then bring your plants inside the greenhouse again so that you can push the growing season into October and November.
Grow them all year round
If you want to grow veggies in your greenhouse all year round, you can but you need to ensure that you monitor all the essentials to ensure your veggies get what they need in terms of light, water, humidity, and temperature.
For example, if you want to grow cool-season vegetables in your greenhouse, you’ll have to ensure you keep the temperature inside between 40 and 50 degrees Fahrenheit.
Transfer your plants at the right time
Grow your seeds until just before the last frost is expected in your area. When the seedlings have reached four inches of growth, you can transplant them into bigger pots. Do the same thing when they reach eight inches.
Then, when the weather warms up outside and it’s warm enough, you can transfer your plants there.
Most veggie plants will need soil temperature that’s between 65 and 75 degrees Fahrenheit, although this will vary depending on whether they’re warm- or cold-season vegetables.
Some Vegetables You Should Start Growing Indoors

Not all veggies should be grown indoors. Some can’t handle being transplanted outside at a later stage. The best veggies that can be grown indoors and then transplanted into the garden with no problems include lettuce.
Other veggies, such as cabbage, are good for starting indoors because they can benefit from a longer growing season.
Then, veggies such as peppers, can thrive by being started indoors or in a greenhouse because they are susceptible to being damaged by the frost. Keeping them inside when there’s frost outside helps to keep them alive and thriving.
Related Questions
Soil temperature plays a role in how plants can draw water and nutrients they need from the soil, and it also influences their root growth.
Raised beds are great because they drain well and they become warm early in the springtime so you can plant in them earlier in the season. Best of all, raised beds resist the growth of weeds.
Conclusion
If you want to start your own veggie garden, whether indoors or outdoors, it’s important to know all about when you should plant your veggies. This varies, as we’ve seen in the article, depending on whether your plants are cool- or warm-season plants.
In this vegetable planting guide, we’ve featured all the important information you need to help you start a successful vegetable garden. Happy harvesting!

